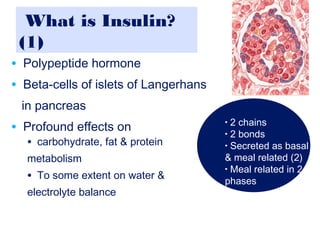
Basal Insulin Is Responsible for Which of the Following Actions
Basal insulin helps glucose control. Insulin suppresses hepatic glucose production stimulates glucose uptake in muscle suppresses adipose tissue lipolysis and fatty acid release into the blood stream.
Insulin Therapy Dr Shahjadaselim
Week 0 Visit 10 11 to receive a BB regimen with mealtime faster aspart or to continue oncedaily basal.
. Increasing glucose concentrations after meals C. Insulin Release from NPH. OBJECTIVE Insulin degludecinsulin aspart IDegAsp is the first combination of a basal insulin with an ultralong duration of action and a rapid-acting insulin in a single injection.
Insulin serves to lower the blood glucose level by stimulating the uptake of glucose by cells specifically muscle cells liver cells and adipose tissue. In general basal insulin. An increase in blood glucose.
Basal insulin is longer-acting and helps keep your glucose levels steady day and night. The primary job of basal insulin is to keep your blood glucose levels stable during periods of fasting such as while youre sleeping. The _____ is the organ responsible for producing atrial natriuretic peptide ANP.
Increase in ketone production. This resorts to the importance of outpatient patient-lead insulin titration. Lack of a standardised insulin dose titration regime may be responsible and unstructured regimens may in turn lead to excessive basal insulin doses and between meal hypoglycaemia.
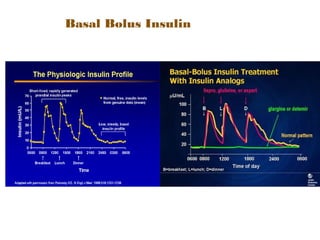
Generally your total daily dosage of injected insulin is split between these short- and longer-acting kinds. Basal Insulins Intermediate and Long-Acting Who. Bolus insulin on the other hand has a much more powerful but shorter-lived effect on blood sugar.
The first-phase insulin release is decreased in the setting of a partial loss of beta-cell mass. Insulin promotes dephosphorylation activation of HMG CoA Reductase HMG CoA Reductase is the control site for the synthesis of cholesterol - it is the enzyme targeted by statins ACAT Acyl CoA cholesterol acyltransferase is also activated by insulin action. _____ causes the destruction of the.
Insulin operates under _____. Following this approach insulin is secreted in a biphasic manner with a first phase of insulin secretion over 15 min generally ascribed to release of insulin from the readily releasable insulin vesicles already docked to the beta-cell membrane. The actions of insulin on the global human metabolism level include.
Insulin stimulates all of the following actions except. What hormones determines the basal metabolic rate at rest when fasting. Basal insulin keeps these glucose levels under control.
Reduction of glucose levels after meals C. Glucose control and hypoglycemia in a 6-month randomized controlled trial. Increase in fatty acid production D.
A key action of insulin in these cells is to stimulate the translocation of glucose transporters molecules that mediate cell uptake of glucose from within the cell to the cell membrane. Background and aims Clinical inertia is reported to delay insulin dose intensification in type 2 diabetes patients. 2 Its designed to stabilize your blood sugar during periods of fasting such as in between meals and while youre asleep.
Basal Insulin Types Benefits Dosage Information And Side Effects. Basal provides a constant supply of insulin to bring down high resting blood glucose levels. Basal insulin absorbs slowly and is long-lasting which helps keep your blood sugar level stable when your liver releases extra glucose.
While fasting your liver continuously secretes glucose into the bloodstream. Basal insulin when used correctly is responsible for which of the following actions. Intermediate- and long-acting basal insulins are recommended for patients with type 1 type 2 or gestational diabetes.
Participants requiring further intensification ie those meeting the randomization criterion of HbA1c 70 to 90 530749 mmolmol following optimization of basal insulin during the runin period were randomized baseline. Increase of cellular intake of certain substances most prominently glucose in muscle and adipose tissue about two-thirds of body cells Increase of DNA replication and protein synthesis via control of amino acid uptake. Summary of the major metabolic actions of insulin.
Suppression glucose production in the liver B. The primary job of basal insulin is to keep your blood glucose levels stable during periods of fasting such as while youre sleeping. New insulin glargine 300 UmL versus glargine 100 UmL in people with type 2 diabetes using oral agents and basal insulin.
Basal insulin is responsible for which of the following actions. Objective We aim to investigate the difference of basal insulin titration methods in reducing HbA1c among the T2DM patients. Modification of the activity of numerous enzymes.
Like other protein hormones insulin binds to specific receptors on the outer membrane of its target cells thereby activating metabolic processes within the cells. They may also be used in other types of diabetes ie. Different guidelines from local and international showed different basal insulin titration method in achieving ideal fasting blood sugar.
Persons with type 1 diabetes generally use intermediate-acting insulin or long-acting insulin in conjunction with regular or rapid acting. Basal insulin is an important component in diabetes management because it acts as a background insulin. Suppressing glucose production by the liver B.
It keeps glucose levels constant throughout the day and night. Suppresses hepatic apolipoprotein B-100 and triglyceride secretion stimulates lipoprotein lipase activity in adipose tissue and inhibits protein. The insulin reaches the bloodstream several hours after injection.
Reducing production of fatty acids D. The basal insulin is responsible for 50 of the total daily insulin output and is an important player in the long-term management of diabetic complications 2.
Basal Bolus What Is Basal Insulin Bolus Insulin
Insulin Therapy Dr Shahjadaselim

Insulin Pharmacology Therapeutic Regimens And Principles Of Intensive Insulin Therapy Endotext Ncbi Bookshelf

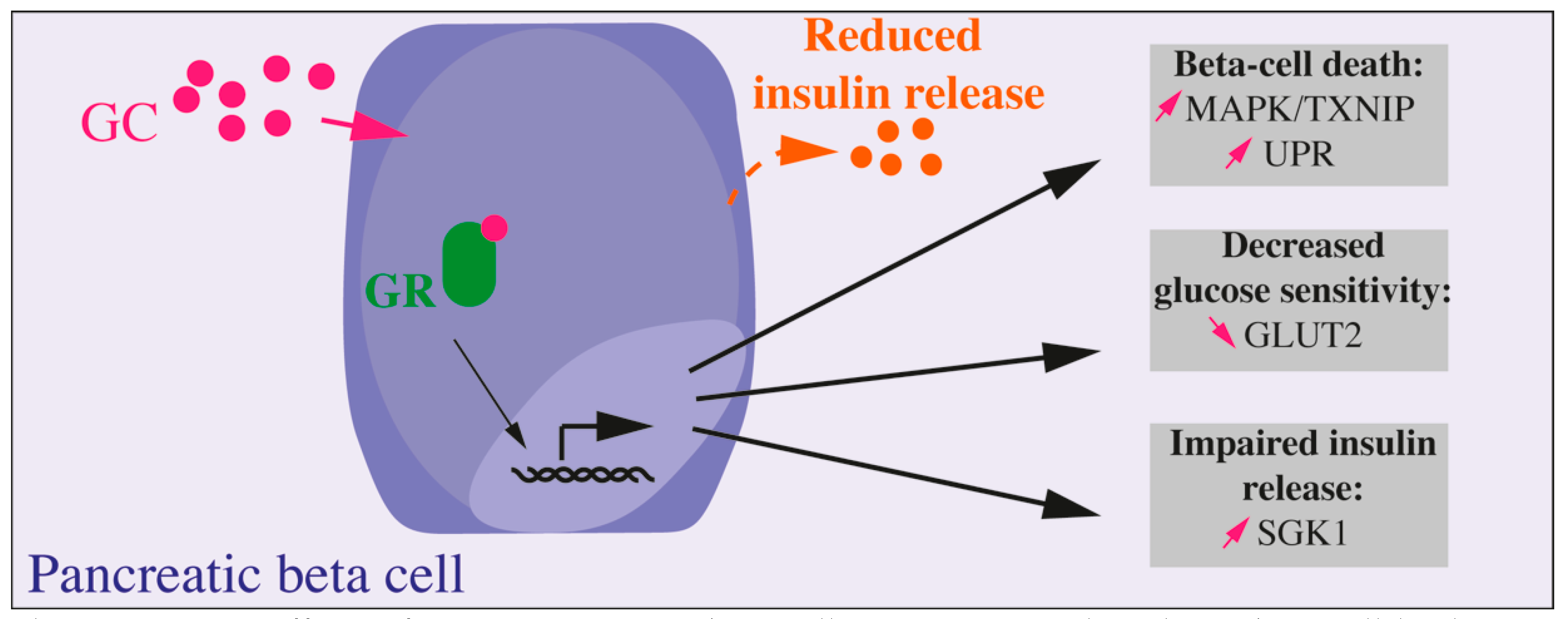
Ijms Free Full Text Molecular Mechanisms Of Glucocorticoid Induced Insulin Resistance Html
No comments for "Basal Insulin Is Responsible for Which of the Following Actions"
Post a Comment